

Our newest infographics guide you through what characteristics make these actions reportable.
Reports in the National Practitioner Data Bank are records of actions taken by authorized organizations regarding health care practitioners, entities, providers, and suppliers who do not meet professional standards. Health care organizations must register with the NPDB and be authorized to report to the NPDB in accordance with the federal regulations. Reports are permanently stored in the NPDB unless modified or removed by the organization that submitted the report.
Reportable actions include medical malpractice payments and health care-related adverse actions. Chapter E of the NPDB Guidebook explains the NPDB reporting guidelines.
Reports are submitted online using the NPDB's secure system, either through the NPDB website or through external applications using the Querying and Reporting XML Service (QRXS).
Before reporting, eligible entities must first register and determine their eligibility under the laws and regulations that govern the NPDB.
Entities must complete the registration process. See the NPDB Guidebook for a full list of eligible entities.
Federal regulations determine the types of actions that are eligible to be reported and/or are required to be reported. Actions are reportable regardless of whether they are being appealed.
Reports must be submitted within 30 days of the date an action was taken or a medical malpractice payment was made.
Organizations that are registered with the NPDB, and are eligible to query, may view reports.
NPDB information is intended to be used in combination with information from other sources when entities are making decisions regarding licensure, employment, contracting, membership or clinical privileges, or when conducting investigations. Health care practitioners and organizations can request their own information from the NPDB by ordering a Self-Query.
Plaintiff's attorneys can request information from the NPDB under specific circumstances.

An Initial Report is the first report of a medical malpractice payment, adverse action, or judgment or conviction submitted to and processed by the NPDB.

A Correction amends an error or omission in a previously submitted report. The reporting entity must submit a Correction as soon as they discover an error or omission is present.
A Correction replaces the previously submitted report it is amending and can be submitted as often as necessary.

A Revision-to-Action is a modification to an action that has already been reported. In other words, it is a report of an additional or continuing action that is related to a previously reported action.
A Revision-to-Action does not replace the preceding report(s), rather, it becomes an additional part of the disclosable record.
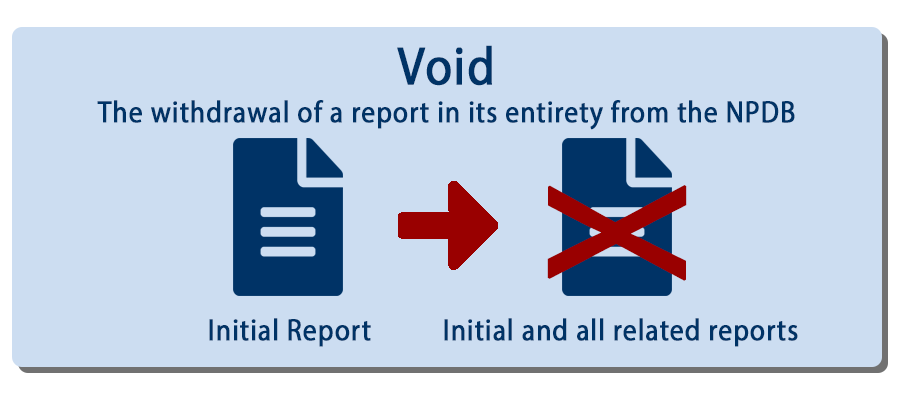
A Void is the withdrawal of a report in its entirety from the NPDB. When a report is voided it is removed from the disclosable record of the report subject.
A reporting entity may void a report at any time.